8 Things To Know About Radiant Heating
Radiant heating is commonly referred to as a heating system installed under floor covering. It can be an electric pad installed under floor tile, or circulating hot water.
There are two above floor methods of installing radiant heating that utilize hot water. The old-fashioned system uses steam that is circulated through pipes and cast iron radiators. Today, this system has been modified to use hot water, distributing heat through small baseboard radiators.
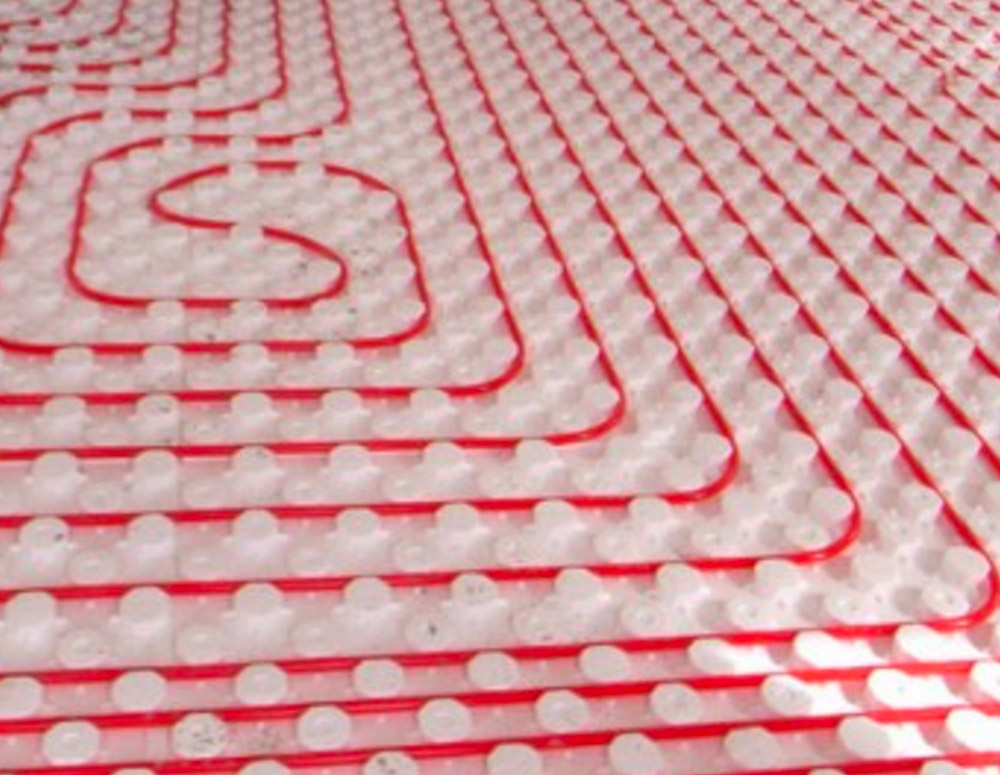
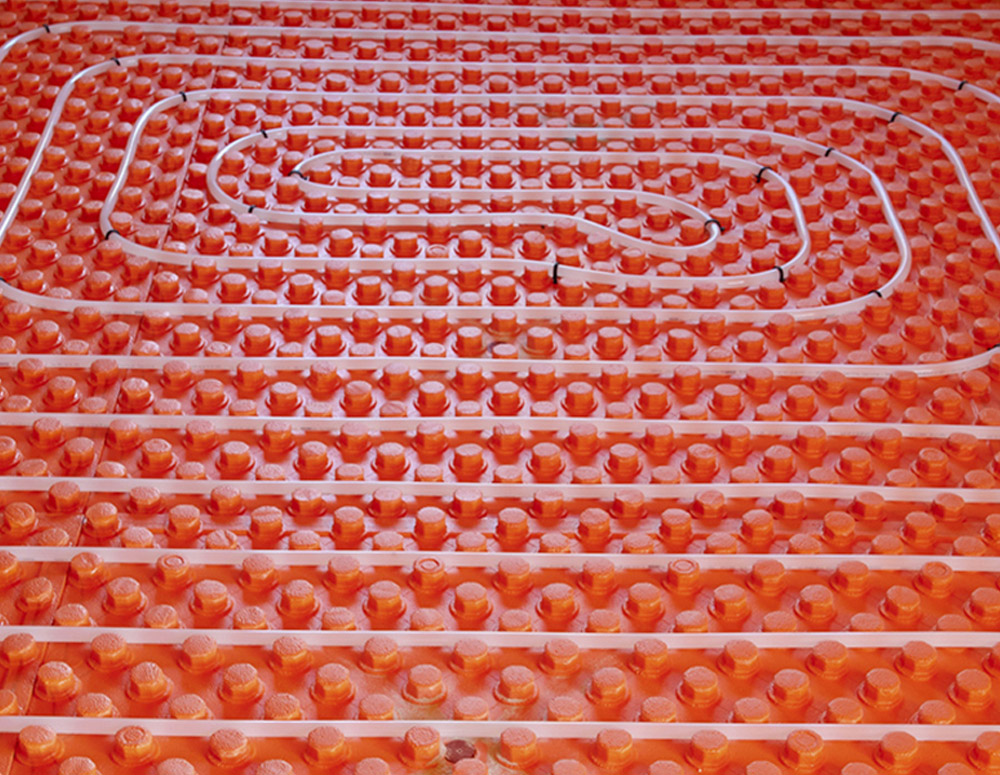
A MORE POPULAR SYSTEM is the distribution of hot water inside of special tubes under the floor covering or inside walls. This system is by far the most efficient installation, delivers heat more uniformly and is the most desirable option.
System Components
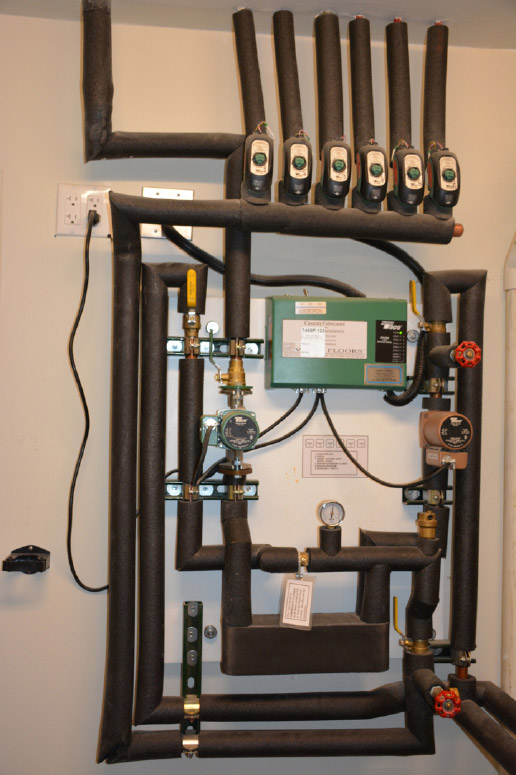
1. A radiant heating system is composed of a boiler to heat the water, retention tank to contain the hot water, a set of manifolds and controls for distribution of hot water, and the tubing system that delivers hot water to floor areas, called PEX Tubing.
2. The boiler and the retention tank can be either separate equipment or combined in one unit like a residential water heater. Both systems work well. The selection of one system over the other can depend on the amount of area being heated, budget and other considerations such as location and the size of the mechanical room housing the equipment. Currently, it is even possible to use DEMAND or TANKLESS Water heaters for radiant heating if desired.
3. The selection of controls, and the engineering of distribution, zoning and programing are integral in how well the system works. This is when a professional installer’s knowledge is invaluable.
Systems in New Construction
4. When a new building is under construction and the floors and subfloors are open, the tubes are installed on the subfloor with a predetermined configuration. Then the tubes are covered with Gyp-Crete underlayment or mortar. Gyp-Crete is a lightweight underlayment material with high compressive strength. It will serve as a protection cover for the tubes as well as a medium for the distribution of heat. It will accept most floor coverings such as tile and wood.
5. When hardwood floor is being installed over radiant heating, it is highly advisable to use engineered flooring rather than solid wood. Solid wood will have the tendency to dry up and shrink in close proximity to heat. Engineered flooring is more stable.
Retrofit Systems in Existing Homes
6. When retrofitting an existing home, often the tubes are distributed in the joist cavity, below the subfloor. This is not the most efficient installation, but when other options are not available, this system can be designed and installed such that it would function well.
7. It is possible to design and install one system that can deliver heat through tubing installed in the floor cavity as well as through baseboard radiators. This system is often used in retrofitting existing homes where access is limited and removal of floor covering and ceilings have restrictions. In this situation, the installer would need to design the zoning with proper attention to the temperature delivered to the different radiators and floor tubing.
Why pay a Professional
8. The PROPER installation of radiant heating system requires thorough knowledge of the technology involved. The technology improves regularly and multitudes of systems, components and products are available for specific applications. When selecting an installer, it is essential that the installer would be specialized in the radiant heating, design, engineering and installation, and would have years of experience.